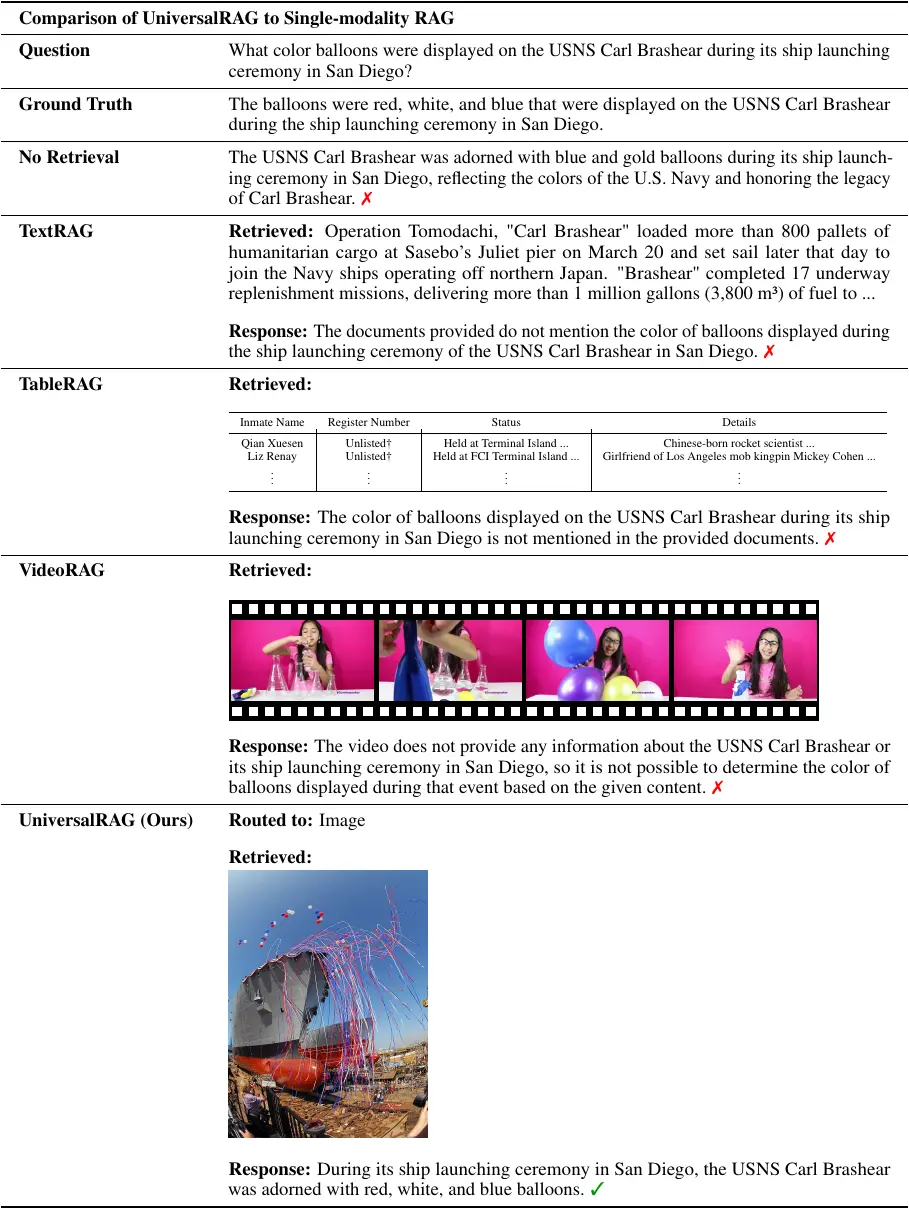
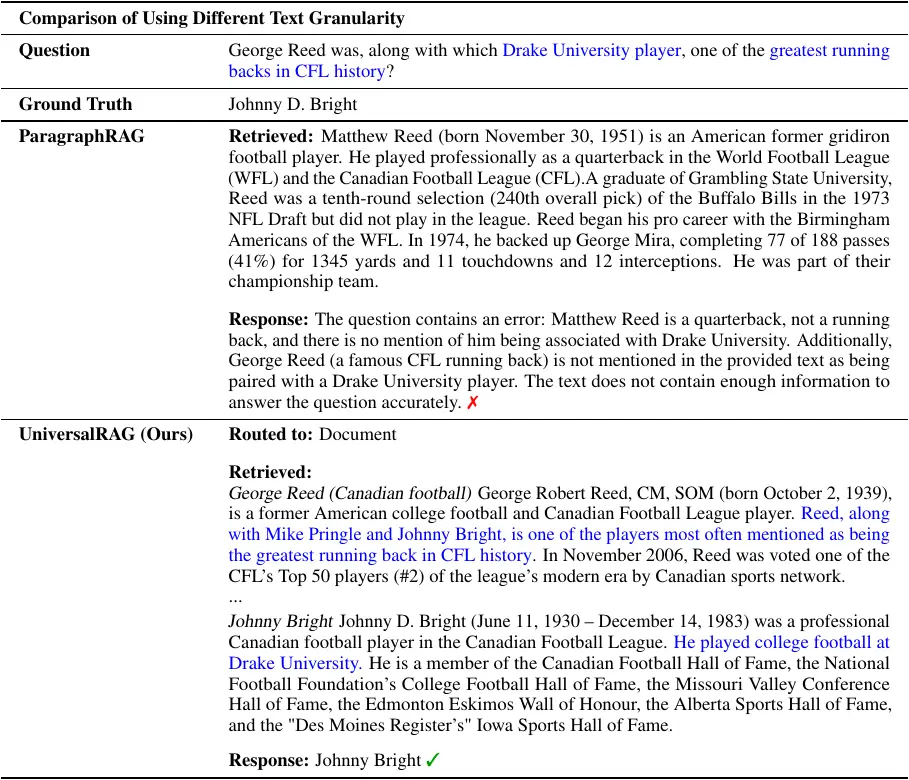
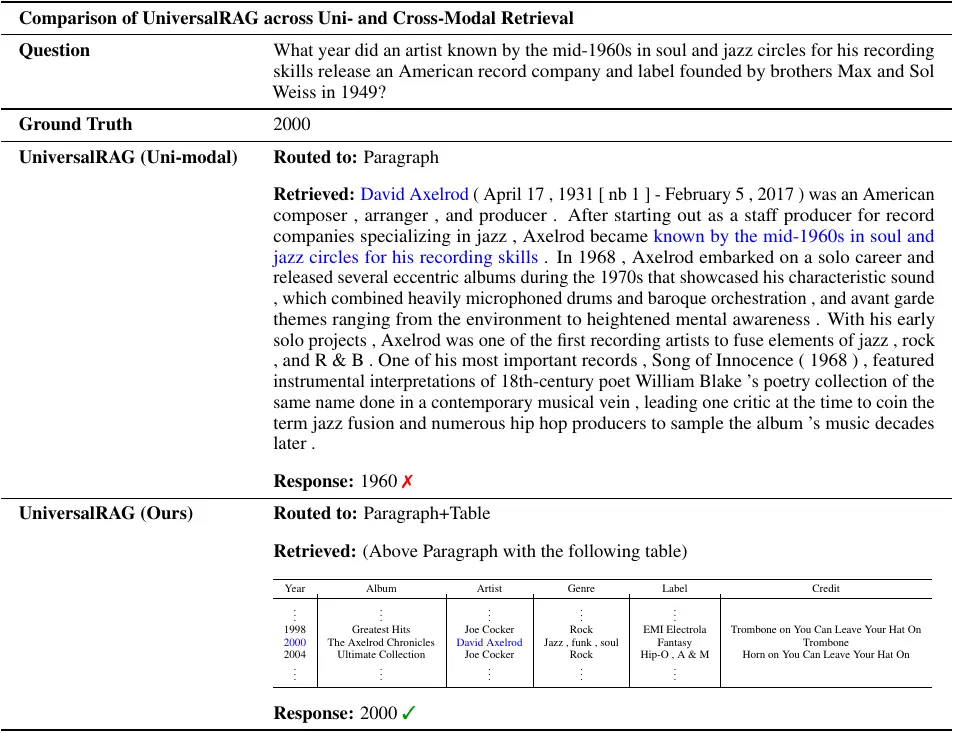
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has shown substantial promise in improving factual accuracy by grounding model responses with external knowledge relevant to queries. However, most existing approaches are limited to a text-only corpus, and while recent efforts have extended RAG to other modalities such as images and videos, they typically operate over a single modality-specific corpus. In contrast, real-world queries vary widely in the type of knowledge they require, which a single type of knowledge source cannot address. To address this, we introduce UniversalRAG, designed to retrieve and integrate knowledge from heterogeneous sources with diverse modalities and granularities. Specifically, motivated by the observation that forcing all modalities into a unified representation space derived from a single aggregated corpus causes a modality gap, where the retrieval tends to favor items from the same modality as the query, we propose modality-aware routing, which dynamically identifies the most appropriate modality-specific corpus and performs targeted retrieval within it, and further justify its effectiveness with a theoretical analysis. Moreover, beyond modality, we organize each modality into multiple granularity levels, enabling fine-tuned retrieval tailored to the complexity and scope of the query. We validate UniversalRAG on 10 benchmarks of multiple modalities, showing its superiority over various modality-specific and unified baselines.
UniversalRAG: Retrieval-Augmented Generation over Corpora of Diverse Modalities and Granularities
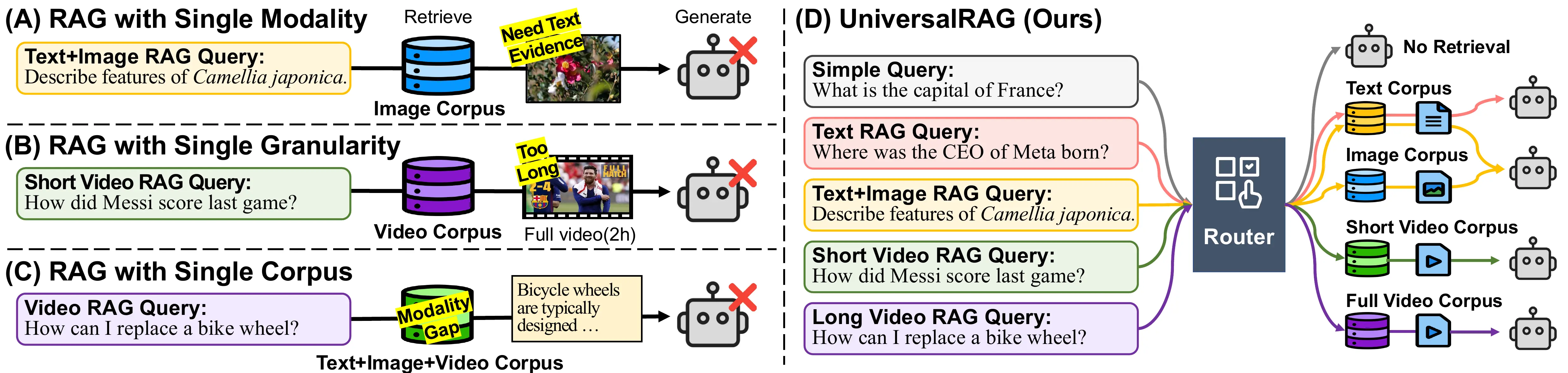
Conceptual illustration comparing existing RAG strategies with our proposed UniversalRAG.
- RAG with Single Modality struggles to handle queries requiring modalities other than one in the corpus.
- RAG with Single Granularity lacks flexibility in granularity, resulting in overly fine or overly coarse information.
- RAG with Single Unified Corpus causes modality gaps that bias retrieval toward the modality of the query.
- Our UniversalRAG overcomes these limitations via a modality- and granularity-aware routing mechanism over diverse corpora.
Why UniversalRAG?
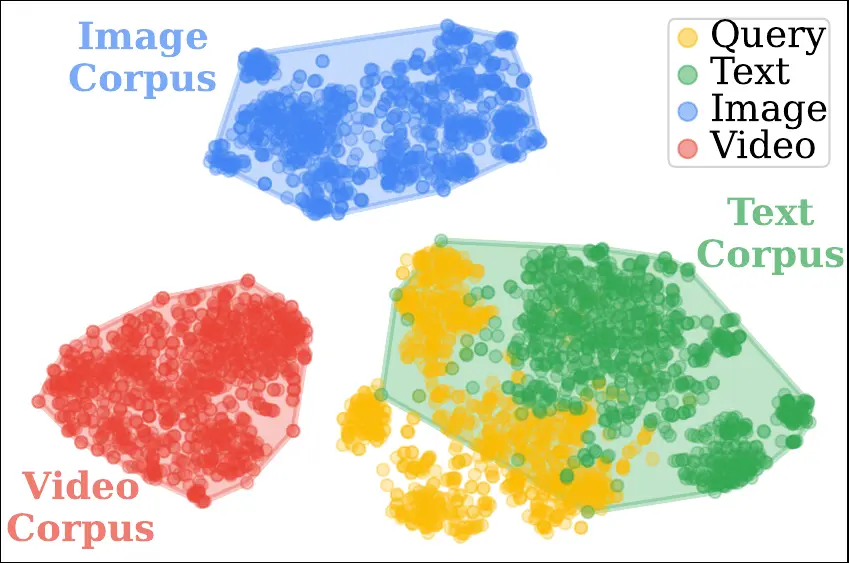
Can multimodal content be effectively retrieved from a single unified embedding space? Multimodal encoders are trained to align semantically similar content across text, images, and videos, yet a persistent modality gap remains: embeddings tend to cluster by modality rather than meaning, as illustrated in Figure 1. This separation limits cross-modal retrieval as queries are implicitly routed by modality instead of true semantic similarity.
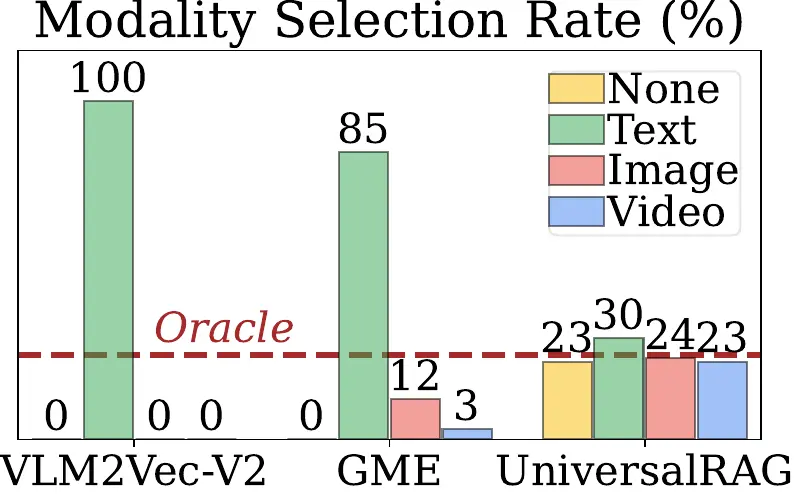
UniversalRAG addresses this challenge through modality-aware routing. Rather than forcing heterogeneous data into a single shared space, UniversalRAG dynamically identifies the most relevant modality-specific corpus and performs targeted retrieval within it. This design sidesteps the modality gap while remaining flexible to the introduction of new modalities. Beyond modality, UniversalRAG further organizes each corpus by granularity—from passages to full documents, or from short clips to full videos—so the retrieval process matches both the semantic intent and the scope of the user’s query. As shown in Figure 2, UniversalRAG yields a balanced distribution of retrieved items across modalities, automatically selecting the most appropriate knowledge source for each query.
Results
We evaluate UniversalRAG on a comprehensive benchmark covering 10 datasets that span multiple modalities and granularities. The full results in Table 1 and the averaged performance across different LVLMs in Figure 3 indicate that, UniversalRAG outperforms strong unimodal and multimodal RAG baselines, validating the effectiveness of our modality- and granularity-aware routing.
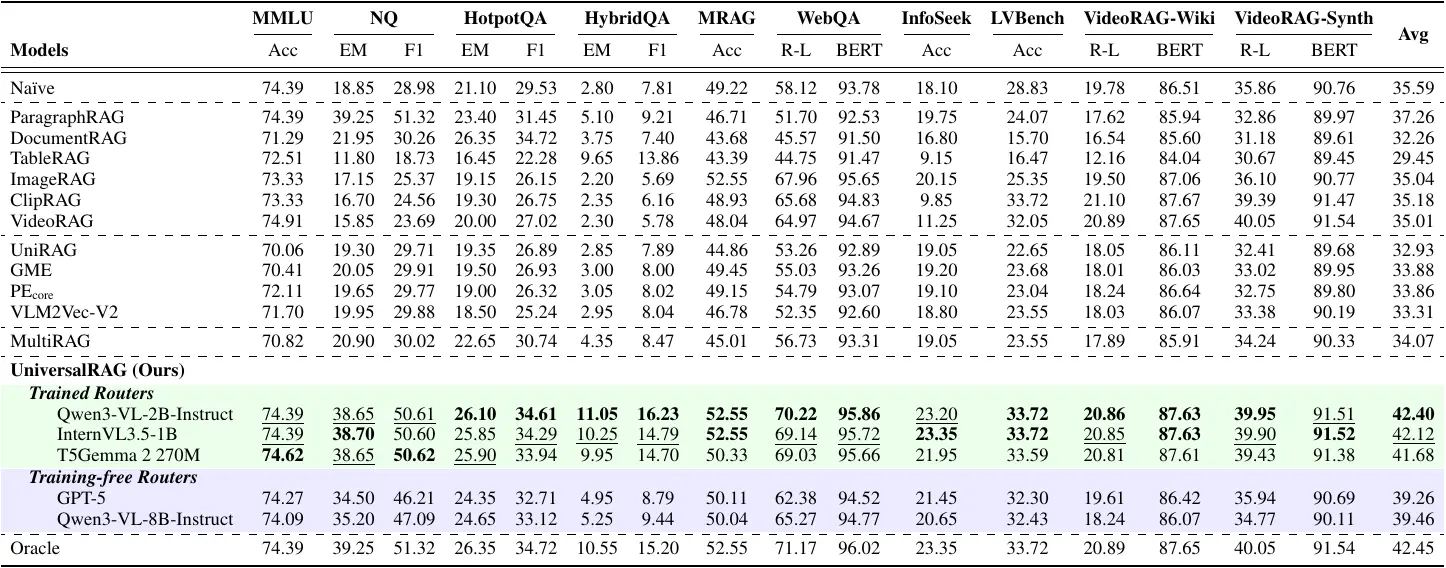
Table 1. Results of diverse RAG methods with Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct across modalities. Bold denotes the best performance and underlined indicates the second-best among UniversalRAG variants, using either trained or training-free routers.
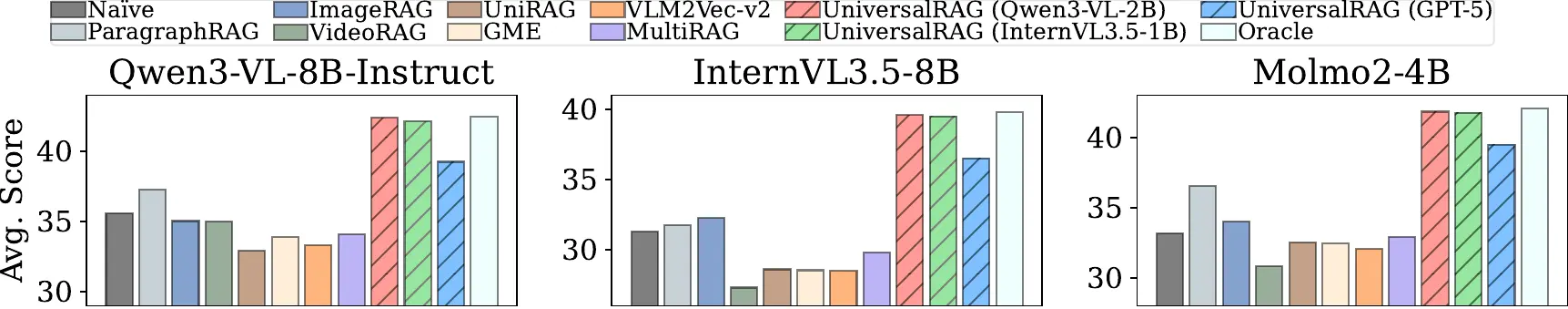
Figure 3. Comparison of averaged evaluation results across different RAG methods and LVLMs.
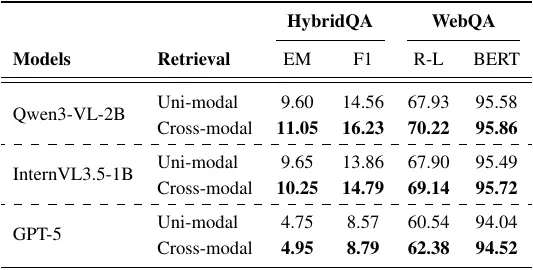
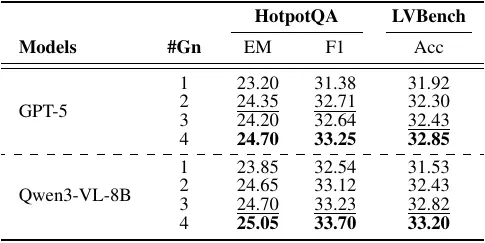
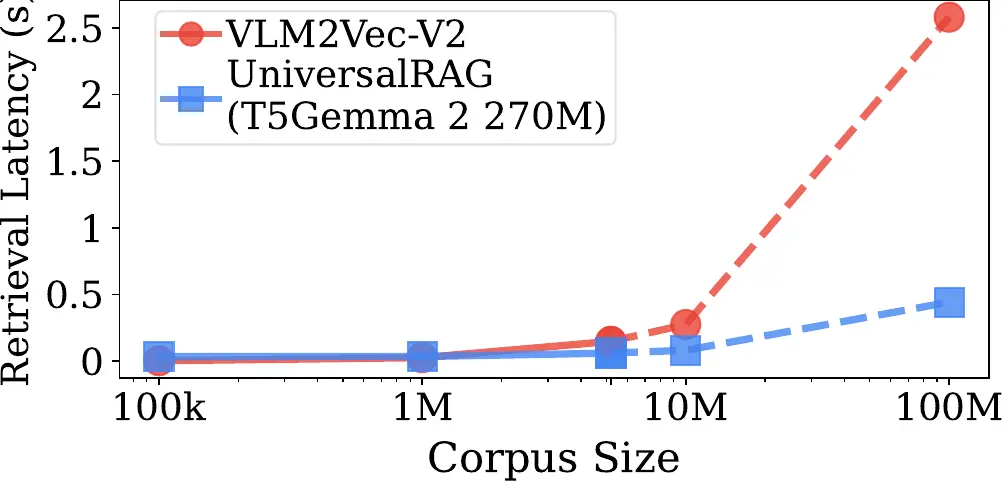
We further conduct ablation studies to validate the effectiveness of UniversalRAG’s granularity-aware routing and cross-modal retrieval, and additionally demonstrate its efficiency in real-world usage scenarios.
BibTeX
@article{yeo2025universalrag,
title={UniversalRAG: Retrieval-Augmented Generation over Corpora of Diverse Modalities and Granularities},
author={Yeo, Woongyeong and Kim, Kangsan and Jeong, Soyeong and Baek, Jinheon and Hwang, Sung Ju},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2504.20734},
year={2025}
}